In an era where digital transformation is reshaping industries, agriculture is not left behind. The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in this age-old sector is a remarkable example of how technology can revolutionize traditional practices.
IoT in agriculture represents a significant leap towards smarter, more efficient, and sustainable farming methods.
This blog post aims to delve into the transformative role of IoT in agriculture, exploring how it enhances productivity, optimizes resource use, and addresses challenges faced by the agricultural sector in the digital age.
Overview of IoT in Agriculture

The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized various sectors worldwide, including agriculture. In agriculture, IoT technologies integrate advanced sensors, connectivity, data analytics, and automation to foster more efficient and eco-friendly farming practices.
- Smart Sensors: These devices collect data from the environment such as soil moisture, crop health, and weather conditions. For instance, IoT-enabled smart sensors monitor crucial physical factors for crop growth.
- Autonomous Equipment: IoT technology facilitates the use of drones and robots for tasks like planting, weeding, and harvesting, vastly improving operational efficiency and precision.
Their prime objective is to enhance agricultural productivity while minimizing waste and resource use. Through real-time monitoring and predictive analysis, farmers can make data-informed decisions, leading to improved crop yields and reduced environmental impact.
However, while IoT has impressive benefits and can truly speed up digital transformation, it also brings challenges for companies in the ag sector, such as digital literacy, infrastructure investment, and data security.
We’ll discuss these challenges in more detail below, as knowing these can help stakeholders prepare for a smooth integration of IoT solutions in agricultural practices.
Applications of IoT in Agriculture

As we delve into different applications of IoT in agriculture, it’s essential to explore how these cutting-edge technologies are being utilized to reshape and enhance farming practices.
From smart sensors in crop fields to advanced data analytics for livestock management, each application underscores the profound impact of IoT on modern agriculture.
Precision Farming
Precision farming leverages IoT to bring about highly efficient, data-driven agricultural practices. For example, CropMetrics (CropX) specializes precision irrigation management. They utilize advanced sensors and data analytics to precisely determine water and fertilizer requirements, optimizing resource use and boosting crop yields.
Agricultural drones, discussed below, represent another facet of precision farming, providing detailed insights into crop health, irrigation needs, and pest management through aerial monitoring. These drones gather comprehensive data, including multispectral and thermal imagery, to aid in decision-making and improve overall farm productivity.
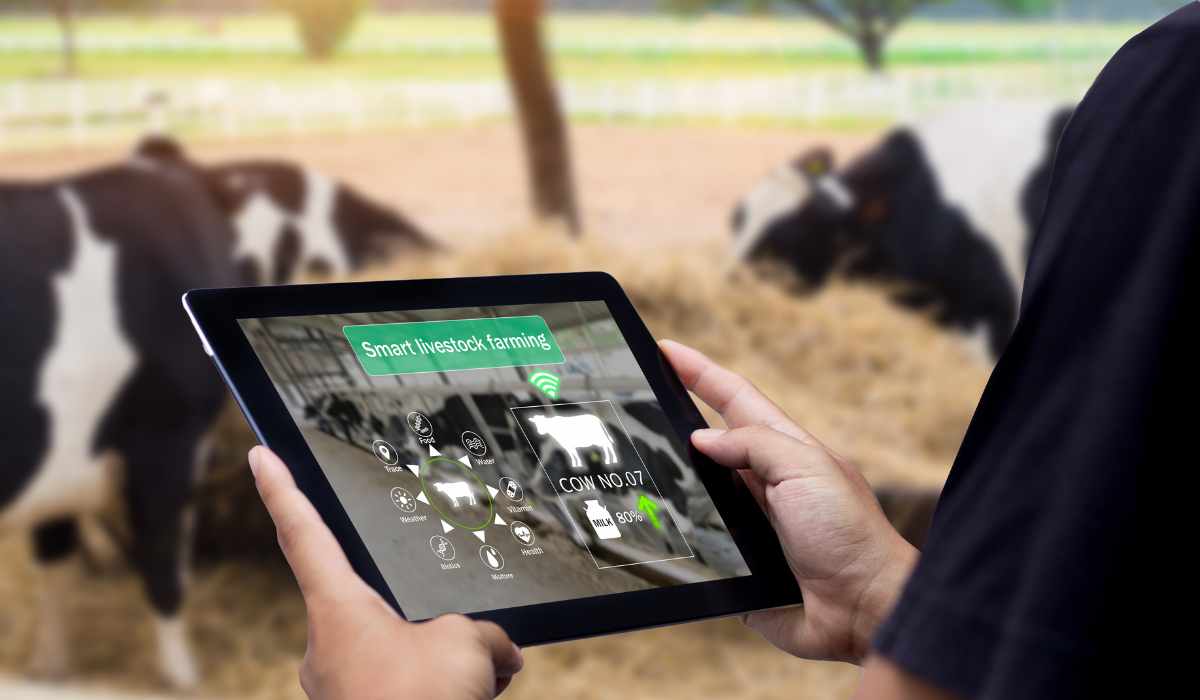
Livestock Monitoring
IoT devices contribute to livestock monitoring by providing real-time data about the health and location of cattle. For example, wearable sensors can track an animal’s vitals and activities, alerting farmers to any signs of distress or illness, which enables timely intervention to prevent livestock diseases from spreading.
Further, IoT technology solutions like u-blox can transfer real-time location data to a management platform, detect changes in animal behavior, and enable fenceless farming. Another example is Moocall, which offers sensors for monitoring calving and heat in cattle, sending alerts to farmers for timely intervention.
Smart Greenhouses
Smart greenhouses use IoT to autonomously monitor and control climate conditions, which can lead to significant energy savings. Sensors within the greenhouse can adjust lighting, temperature, and humidity levels, creating an optimal environment for plant growth without manual intervention.
For instance, climate control systems from companies like Climate Control Systems Inc automate greenhouse environments, managing heating, cooling, and irrigation. This reduces operational costs and enhances plant growth.
Another potential application is the integration of AI and sensor-based systems for frost prediction and management, crucial for protecting crops during adverse conditions.
Supply Chain Optimization
Beyond the farm, IoT enhances supply chain management by tracking the movement of goods from farm to table. This improves inventory management, reduces waste, and ensures timely delivery of products, increasing transparency and trust among consumers.
Key Technologies

In the realm of smart farming, certain technologies have become pivotal for their effectiveness and ability to transform agricultural practices. These technologies have enabled farmers to monitor, control, and optimize their operations with unprecedented precision.
Sensors
Agricultural sensors facilitate a range of farm activities by providing vital data regarding soil moisture levels, climate conditions, and crop health. For instance, integrated soil sensors aid in the precise application of water and fertilizers, making operations more efficient and sustainable.
Drones
Drones have taken precision agriculture to new heights; they are instrumental in field mapping and monitoring crop health from above. With advanced imaging capabilities, farmers can now analyze crop vigor and detect issues like pest infestations early on.
Automated Irrigation Systems
Through the use of automated irrigation systems, water resource management has become highly efficient. These systems can adjust water delivery based on real-time data from sensors, ensuring optimal irrigation without waste.
Data Analytics
Finally, data analytics play a crucial role by turning vast amounts of collected farm data into actionable insights. This helps farmers make informed decisions, leading to increased productivity and reduced costs. By leveraging data analytics, they can track and forecast various agricultural variables effectively.
Benefits of IoT in Agriculture

As mentioned, the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into agriculture translates into tangible benefits such as enhanced crop yields, improved resource management, and a bolstered commitment to sustainability practices.
Increased Crop Yield
Employing IoT technologies in agriculture paves the way for more precise farming techniques. Sensors can monitor crop conditions in real time, enabling farmers to make more informed decisions. A benefit of precision farming is the capacity to adjust variables like water, fertilizer, and pesticides to suit the exact needs of each crop, which can lead to increased yields.
Resource Optimization
IoT devices have a significant role in the efficient usage of resources such as water, electricity, and fuel. Smart irrigation systems ensure water is used judiciously by irrigating only when necessary. In addition, the automation of equipment and machinery reduces downtime and maintenance costs while improving overall efficiency.
Sustainability
By optimizing inputs and reducing waste, IoT contributes to more sustainable agricultural practices. It helps to minimize the environmental footprint of farming operations by decreasing the overuse of fertilizers and chemicals.
Challenges and Considerations
In the integration of IoT in agriculture, stakeholders face specific hurdles and must contemplate various factors to ensure successful deployment.
Data Security and Privacy
IoT applications in agriculture collect vast amounts of sensitive data, making data security and privacy a crucial concern. An IoT-based smart farming system must incorporate robust mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access and protect against data breaches, which can expose farm operational details and personal information of farmers.
Cost and Investment
The initial cost and investment required to implement IoT solutions in agriculture are substantial. The expenses encompass not only the hardware like sensors and drones but also the software for data analysis and storage. Maintaining this technology over time adds to the financial considerations for farmers and agribusinesses.
Technology Adoption Barriers
Lastly, there are significant technology adoption barriers in agriculture. These include a lack of digital literacy among farmers, the heterogeneity of farms, and an uncertainty regarding the return on investment. Moreover, resistance to change and differing regional regulations can impede the uptake of IoT innovations in the sector.
Despite these challenges, as IoT continues to evolve, it promises to further revolutionize agriculture, enhancing food security and environmental stewardship for generations to come.
Further Reading:
- Internet of Things (IoT) based Smart Agriculture Aiming to
Achieve Sustainable Goals (arXiv – Cornell University) - Smart Farming: Internet of Things (IoT)-Based Sustainable Agriculture (MDPI)
- IoT for Agriculture (NIST)